The possibilities of technical improvement of the engine are directly dependent on the functional properties of engine oil. Modern lubricants are able to withstand high mechanical and thermal loads for a long time, protect against wear, corrosion and deposits that disrupt the normal operation of the unit and reduce energy losses.
Lubricating oil quality can be improved in two ways:
Improving the properties of the base oil (base oil) upon its receipt;
Alloying oil with additives.
Improvement of oil production technology using effective purification processes, molecular conversion of oil molecules, synthesis of new oils, can significantly improve some operational parameters. The properties of oils can be greatly improved by adding additives to the base oil. Oil improved with additives is called compounded or alloyed oil (blended oil, compounded oil, formulated oil). By varying the composition of base oil components and additive compositions, lubricant developers can create oils that meet the diverse requirements of manufacturers of mechanisms and equipment, as well as form a wide range of lubricants with differentiated properties to solve diverse, sometimes very specific and even contradictory, tasks of lubricating engines and transmission units. . The descriptions of a commercial product - lubricating oil, as a rule, list the main methods of its production, technologies for improving the base oil, as well as a list of the most important additives.
Additives(additives) - synthetic chemical compounds introduced into the base oil to improve properties during periods of operation and storage. Almost all commercial automotive oils are produced with additives, their number reaches up to 8 different compounds, and the total mass content is up to 25%. Almost all additives, both single and packaged, are supplied to oil blending plants in the form of additive solutions in oil containing about 50% active substance. The recipes indicate not the content of the pure additive, but the amount of the commercial product of the additive, i.e. its solution. Therefore, the indication of the presence of 25% additives in the oil does not yet indicate the actual amount of active substances. When analyzing finished or working oils, the consumption of additives is determined and the content of active elements of additives (active element content) is calculated.
Some additives affect the physical properties of base oils, others have a chemical effect. They can complement each other, which creates a synergistic effect, but they can also cause an antagonistic effect. Many modern additives perform several functions (multifunctional additives). Additive compositions are most often supplied to the market - packages (additive package). These are packages of a strictly defined composition, designed for oil of a specific purpose and quality class.
Thus, if there are ready-made additive packages and various base oils on the market, it is possible to obtain commercial oils with a certain and constant level of performance properties using simple technological methods - dosage and mixing. American and European quality assurance systems in their documents (API documents and the ATIEL Code of Practice) provide for simplified and cheaper test procedures for such compounded oils when assigning a quality class and granting the right to designate API or ACEA class marks. This allows small firms (oil blending plants) to produce and supply automotive oils of controlled and sufficient quality at the lowest cost. The development of a coordinated composition of the package, in which full compatibility (compatibility) and synergistic interaction (synergism) of individual additives would be achieved, is a complex and time-consuming process that requires a large scientific and technical potential. Large oil companies are engaged in the production of additive packages ("Shell Additive" + "Paramins" ("Exxon") = "Infenium", "Texaco Additive", "Oronite" ("Chevron"), etc.) and chemical companies ("Lubrizol", "Ethyl", "BASF", etc.) Due to the danger of imbalance of additives, LARGE OIL COMPANIES AND CAR MANUFACTURERS LOOK NEGATIVELY AT THE USE of additional additives poured into the crankcase of a car (aftermarket additives). Additive packages are supplied as a concentrated solution of additives in oil (up to 50% of active substances). Such a composition is introduced into the base oil and after mixing, a commercial oil is obtained, ready for use. In practice, such production is carried out at mixing plants (blending plant). Mixing of components is carried out either batchwise in large tanks (batch blending) or continuously by introducing the components into the main stream of the oil mixing line (line blending, in-line blending). The finished oil is sent for packaging. There are about 400 oil mixing plants in Europe. They are independent, have their own trademarks, or belong to large oil companies. These are well-equipped factories, automatically controlled, with laboratories for product quality control. The high quality of the products can be guaranteed by the automatic mixing control and the consistency of the suppliers of base oils and additives. Any replacement of base oils or other components requires, without fail, additional procedures for checking the quality of the oil. Such a check is regulated by the relevant documents - in Europe, the ATIEL Code of Practice (The ATIEL Code of Practice) and the ATC Code of Practice (ATC Code of Practice), and in America - the API System for Licensing and Certification of Motor Oils "(API Engine Oil Licensing and Certification System) and the "CMA Code of Practice" (LSU Code of Practice). Oil blending companies are trying to obtain quality certificates from ISO, Lloyd (Lloyd) and other reputable organizations. The sign of the received certificate is applied to the product packaging as proof of the high quality of production and product control.
Additive action.
Additives can:
To give the oil new properties (the formation of a chemisorption sulfide or phosphide film on the rubbing surfaces of parts that prevents wear);
Improve the existing properties of the oil (reduce the viscosity-temperature dependence, lower the pour point);
Slow down or stop undesirable processes occurring during the operation of the oil (slow down oxidation, sludge formation, metal corrosion).
The effectiveness of additives is determined by their chemical properties and concentration in lubricants, as well as the pickup of the latter to additives, because some additives are more active in some base oils than in others.
Additives must:
Dissolves well in oil;
Possess low volatility and do not evaporate from the oil during storage and operation in a wide temperature range;
Do not wash out with water and do not undergo hydrolysis;
Do not interact with contact surfaces of materials;
Maintain their functions in the presence of other additives and not have a depressive effect on them.
In practice, additives are classified according to their functional action.
According to the main purpose (defining property), additives are conditionally combined into several groups:
Viscosity additives that improve the viscosity index and other properties (viscosity index modifiers, depressants);
Additives that improve lubricity (friction modifiers, antifriction, friction, antiwear, extreme pressure, tackiness, antipitting, metal cladding, etc.);
Antioxidant additives that reduce oil consumption and increase the service life of the oil (antioxidants);
Anti-corrosion additives (corrosion inhibitors);
Detergent additives (detergents);
Other additives (anti-foam, etc.)
Most modern additives are multifunctional, i.e. have several useful properties, For example, detergent additives are also anti-corrosive. The ratio of the action of complex properties is regulated by the chemical structure of the additive.
In this section, additives intended for mineral and polyalphaolefin oils will be considered mainly. For synthetic base oils, other additives and in different proportions can be used.
Viscosity additives.
Viscosity additives are used to improve the viscosity-temperature characteristics. In foreign literature, they are called viscosity index improvers or viscosity index modifiers (viscosity index improvers, viscosity index modifiers - VIM). Pour point depressants also belong to viscosity additives. Their action is based on the suppression of gelation at low temperature resulting from the crystallization of paraffin.
Viscosity modifiers (VM).Multigrade oils should have a low temperature dependence of viscosity, i.e. The oil must be sufficiently fluid at low temperatures and sufficiently viscous at high temperatures. This is achieved by introducing viscosity additives - polymeric thickeners. At low temperatures, when the oil is viscous, the polymer molecules are, as in a poor solvent, in a twisted form and have little effect on the viscosity. With increasing temperature, their solubility increases, they unwind and increase the viscosity of the oil (compensate for the significant loss of viscosity of the oil itself with increasing temperature). Thus, the dependence of the oil viscosity on temperature is suppressed (the viscosity index increases). Additives with such properties are called viscosity index improvers, however, in foreign literature, the term "viscosity modifier" is now more often used. As viscosity modifiers, polymers and copolymers are used - polyisobutylene, polymethacrylates, copolymers of olefins (ethylene, propylene, butylene), hydrogenated copolymer of styrene and butadiene, hydrogenated polyisoprene, etc. In order to emphasize their high molecular nature, they are called polymeric viscosity modifiers ).Thickening polymers are currently available as solutions in standard base oil and are marketed labeled as concentrates according to their thickening effect.
Polymer viscosity modifiers are effective in oils operating under moderate loads, in the absence of high shear. Under high load and high shear rate, long thickener molecules can break into small fragments, as a result of which the effectiveness of the thickener during operation gradually decreases. That is why new oils with a high viscosity index, stable for long-term operation under severe conditions, are obtained not only by adding polymer additives, but also by modifying the base oil molecules, for example, by hydrocracking. Oil molecules that are more uniform in length and linear configuration simultaneously have a higher viscosity index and are more resistant to mechanical degradation. These oils are characterized by a constant viscosity over long periods of operation at high temperature and high shear (HTHS). Often they are called oils with stable properties during operation.
Depressants(depressants). With a significant decrease in the temperature of the lubricating oil, paraffin crystals in the form of needles and plates begin to fall out of it with the formation of a spatial crystal lattice, which leads to a loss of oil mobility (gelatinization) and makes it difficult to start the engine at low temperatures. The low temperature fluidity of such oils can be improved by deep dewaxing, however, this results in higher production costs. Therefore, the oils are only partially dewaxed down to a pour point of the order of -15°C. Further lowering of the pour point is achieved by the introduction of pour point depressants, which are able to lower the gelatinization (pour) temperature by another 20 - 30 ° C by suppressing wax crystallization and agglomeration, while they do not prevent the appearance of these crystals. The physical pour point of the entire oil, as a rule, is significantly lower than the crystallization temperature of paraffins - an integral part of the oil. Alkylnaphthalenes, alkylphenols and other polymeric products are used as pour point depressants. The concentration of depressants 0.05 - 1.0%.
Additives that improve lubricity. The action of these additives is due to the formation on the rubbing metal surfaces of various chemical composition protective films.
Anti-wear and anti-friction additives. According to the principle of action, anti-wear additives (anti-wear additives) are divided into three groups:
Antiwear additives that increase stickiness and lubricity (this group also includes friction modifiers);
Extreme pressure additives (extreme pressure - EP);
Solid anti-wear and extreme pressure additives.
Anti-wear additives, increasing stickiness and lubricity (lubricating additives, tackiness agents). Under normal lubrication, due to the interaction of the polar groups of oil molecules with the metal surface, an adsorbed oil film is formed on the friction surfaces. In boundary lubrication, the friction force and wear largely depend on the resistance of this film and the force of interaction of oil molecules with the metal surface, i.e. from the lubricity and stickiness of the oil.
To reduce wear and increase stickiness, anti-wear additives (fatty alcohols, amides, esters, phosphorus compounds, etc.) are introduced into the oil, forming a chemical bond with the metal surface. With the help of such additives, stickiness is improved even at low oil viscosity. The greater the strength of the film formed and the stronger it is bound to the metal surface, the lower the viscosity of the oil can be to achieve the same lubricating effect and reduce wear on parts, and with the use of a less viscous oil, energy losses for pumpability are reduced.
Friction modifiers(friction modifiers). These are additives that regulate frictional properties - the coefficient of friction of lubricated surfaces. In most cases, it is required to reduce friction losses, for example in an engine. However, some transmission units include friction mechanisms - wet-type clutches and brakes, retarders, blockers, synchronizers, etc., which are in oil and should ensure good grip of rubbing surfaces and prevent slippage. In these cases, additives that increase friction are used.
Friction reducing modifiers(friction reducers). To reduce friction losses in the engine, and thus to reduce fuel consumption, additives are introduced into the oil that reduce the coefficient of friction. As such additives, compounds are used, in the molecule of which there is a strong polar group that provides good adhesion and a long linear chain that provides good glide. The use of such additives creates additional opportunities for the creation of "energy-saving" oils ("Fuel Economy oils", API SJ / EC, API SH / EC, APLSH / ECII, ILSAC GF-1, ILSAC GF-2, ILSAC GF-3, ILSAC GF-4).
Friction modifiers(friction enhancers). Such additives simultaneously reduce the possibility of noise and vibrations due to sliding with jumps in the coefficient of friction, which is characteristic in powerful transmission units with wet brakes. Compounds are used as such additives, in the molecule of which there is a strong polar group that provides good adhesion and a short linear part, which under certain conditions provides good adhesion. Such compounds are some detergents, sulfides. These additives are added to oils for hydromechanical transmissions, automatic transmissions, limited slip differentials, etc.
Additives introduced to reduce noise and improve the smoothness of the operation of hydromechanical transmissions are called antinoise additives (antisguawk additives). These are derivatives of natural fatty acids and sulfur, phosphonic acids., In oils intended for mechanisms operating in conditions of limited slip, for example, in oils of a self-locking differential (to suppress jerks and vibrations that occur during operation of the unit), anti-vibration additives (dntichatter additives) are introduced. These are fatty acids, higher alcohols and amines, dialkyl phosphites, etc.
extreme pressure additives, EP additives (EP - extreme pressure additives). The term "extreme loads" and the abbreviation EP (extreme pressure) was introduced in the 1920s by the American Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) to refer to the special load on the gear teeth of transmissions, especially in hypoid gears. The adsorption film can be destroyed as a result of a high load and the resulting heating of the contacting surfaces of the metal (more than 150 - 190°C). As a result, friction and heating of the metal surface increase even more, up to welding, seizing, sticking of parts. Welding can be suppressed by additives containing compounds of sulfur, phosphorus, chlorine, etc., which decompose in places of highest friction and high temperatures with the release of the corresponding active elements that react with the metal and form a sulfide, phosphide, chloride and chemisorption film - a solid lubricant. Such a film is much more resistant than an adsorption film and can protect friction surfaces from wear under heavy load and high temperature conditions. Therefore, additives that form a solid chemisorption film are called separating extreme pressure additives or additives of high ultimate load (extreme pressure - EP). Since the active elements are released from the additives and react with the metal only at the protrusion of the surface, at the points of contact, the process of leveling and polishing takes place. Thus, EP additives are both smoothing and polishing additives. The role of phosphorus and sulfur is somewhat different: phosphorus more evens the surface and reduces wear, while sulfur reduces friction and enhances the separating property of chlorine. In the presence of both of these elements, the oil lubricates well both under heavy load and at high sliding speeds.
Basically, EP additives are designed to increase the load-carrying capacity of gear oils, especially for hypoid gears, industrial oils and greases (leveling and polishing processes are unacceptable for honed surfaces of internal combustion engines and are strictly limited by modern international specifications for motor oils ). An additive of universal action is often used, which has both phosphorus and sulfur in its composition - Zinc dialk dithiophosphate (ZDDP - zinc dialk dithiophosphate). Zinc dialkyldithiophosphate differs not only in extreme pressure, but also in antioxidant, anticorrosive, and other properties. The properties of this additive depend on the structure and size of the radicals (R) and by combining them it is possible to reveal one or the other. For example, the heat resistance of an additive increases as the alkyl chain lengthens. Alkyl compounds are more used as extreme pressure additives, with alkyl (aromatic) radicals, which are characterized by high heat resistance.
The high chemical activity of extreme pressure additives does not always lead to the desired result (with very high chemical activity, a thick film is formed, which is poorly retained on the metal surface). In addition, additives containing highly active chlorine and sulfur compounds can cause corrosion of non-ferrous metals (especially copper alloys), so oils with active extreme pressure additives are more suitable for steel-to-steel friction pairs and must be used for gear synchronization with great care.
The amount and effectiveness of EP additives is a sign of the classification of gear oils according to API, the higher the category (API GL-3, GL-4, GL-5), the greater their concentration.
Solid anti-seize additives (solid additives) - in the form of molybdenum disulfide, polytetrafluoroethylene (fluoroplast, Teflon, PTFE, PTFE) and graphite in oil have a colloidal structure, and form a hard and durable anti-wear and anti-seize film on the surface of rubbing parts. Their critical operating temperature is higher than other anti-friction additives. Friction reduction is achieved due to the easy sliding of the layered additive. Such solid additives are mainly added to improve the lubricity of greases, however, some manufacturers produce oils with molybdenum disulfide. Currently, a large number of preparations are being produced - additives to oils that are poured into the engine crankcase (aftermarket additives). Their basis, as a rule, is one of the solid additives, either a molybdenum compound or polyethylene terephthalate. Both oil companies and car manufacturers look at such additives negatively and do not recommend their use to their customers. However, the demand for such products is increasing, especially from owners of used cars. Particular care should be taken when using additives containing surface-active substances (surfactants) used for cutting metals. The action of these additives is based on the softening of metal surfaces (which leads to a significant reduction in friction and an increase in wear).
Anti-corrosion additives.
Corrosion products of metals in oil, when they get on the friction surfaces, contribute to an increase in the wear of parts. Therefore, additives that suppress corrosion, simultaneously perform the function of anti-wear additives.
Anti-corrosion additives, or corrosion inhibitors, work as follows:
Neutralize acids formed during the oxidation of oil or during the combustion of sour fuel; for this purpose, compounds with alkaline (basic) properties are used;
They form a protective adsorption or chemisorption film that prevents the reaction of acids with the metal surface;
For this purpose, compounds of some organic compounds of sulfur, phosphorus and nitrogen are used;
Sulfur compounds, especially disulfides and polysulfides, can be used as extreme pressure and antiwear additives;
They bind moisture, without which corrosion is impossible. Corrosion inhibitors and antirust additives.
Corrosion inhibitors protect the surface of bearing shells and other non-ferrous metal parts from corrosion and corrosive wear caused by organic acids. The protection mechanism is the formation of a protective film and the neutralization of acids. For these purposes, zinc dialkyldithiophosphate, other sulfur and phosphorus compounds, and additives that differ in extreme pressure properties are used. Anti-rust additives protect steel or cast iron cylinder walls, pistons and piston rings from rusting when exposed to an aqueous acid solution. The protection mechanism is the formation of a strongly adsorbed protective film that protects the metal surface from direct contact with an aqueous acid solution. For this purpose, aminosuccinates and alkali metal sulfonates are used - mainly strong surfactants - detergents. The ability of an oil to resist corrosion and rust is evaluated by various methods when determining other performance properties (bench or engine tests).
Alkaline additives play a special role in suppressing corrosion, especially in diesel engines that use sulphurous fuels. Such additives neutralize sulfur compounds formed during the combustion of fuel, thereby preventing the corrosion process. Metal-containing detergent additives are characterized by high alkalinity.
antioxidant additives. Under operating conditions, at high temperatures and under the influence of atmospheric oxygen, intensive oxidation of oil hydrocarbon compounds occurs, as a result of which its lubricating and other functional properties deteriorate. The resource of additives is consumed and the oil must be replaced. Antioxidant additives (antioxidants, oxidation inhibitors) extend the life of the oil.
The process of oil oxidation is quite complicated. In addition to oxygen and temperature, it is influenced by shear rate, mixing intensity, impurities, metal ions (especially copper and, to a lesser extent, iron, etc.)
When oil is oxidized, the following processes occur, which have a significant impact on operational properties:
An increase in the molecular weight of the compounds that make up the components of the oil, as a result of which the viscosity increases;
Formation of organic acids causing corrosion;
The formation of resinous substances (resins) and carbon particles (carbon), coke (coke), which form varnish deposits (varnish, gum residual) and soot (varnish deposits) on hot surfaces of engine parts (pistons, rings). Such contamination leads to a decrease in heat removal and the occurrence (coking) of the piston rings (ring sticking); - aggregation of resinous substances and carbonaceous particles with the formation of black sludge (black sludge) in the oil itself.
Antioxidant additives(antioxidants), called oxidation inhibitors, inhibit oil oxidation in its initial stage of interaction with the primary products of the oxidation reaction - peroxides, with the formation of inactive compounds that are not capable of continuing the oxidation chain reaction Many antioxidant additives that reduce the formation of acids reduce corrosion , i.e., antioxidant additives are also anti-corrosion additives.
The catalytic effect of metal ions on oil oxidation is suppressed by compounds of another group of antioxidant additives - metal deactivators. Organic compounds (ethylenediamines, organic acids), which bind metal ions into inactive complexes, are used as deactivators. Recently, data have appeared in foreign literature that a small amount of copper ions in motor oils, on the contrary, is an effective antioxidant and is specially introduced into some types of oils. This point should be taken into account when analyzing working or used motor oils.
Phenols and amines, such as ionol, are used as antioxidants - peroxide deactivators, and organic compounds of sulfur, phosphorus and others are used as metal deactivators. Zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate is currently the most common antioxidant. It is also used as an extreme pressure additive. New high-quality motor oils of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate contain up to 1.4%.
Detergent additives
Detergent additives are surface-active substances (surfactants) that prevent agglomeration (sticking) of insoluble oxidation products with their subsequent deposition on engine parts. Detergents according to their action are divided into detergents and dispersants.
Detergents are surfactants with detergent properties that protect the surface of parts from sticking and accumulation of oxidation products on them. Anionic detergents are usually oil-soluble alkylbenzenesulfonates, phosphonates and other similar compounds. Some sulfonates have alkaline properties and are effective neutralizers of acidic oxidation products. By alkalinity, which characterizes the effectiveness of additives, sulfonates are divided into neutral (10 - 30 mg KOH / g), alkaline (30 - 100 mg KOH / g), and very alkaline (100 - 300 mg KOH / g). Very alkaline additives may contain dispersed metal oxides, hydroxides and carbonates. Alkaline additives are needed in diesel oils in order to neutralize sulfuric acid, which is formed during the combustion of sulphurous diesel fuel.
Sulfonates, phosphonates, and other detergents are metal salts, so when burned, they form a noticeable amount of ash. Such additives are called high-ash (ash containing additives). At present, along with these, new organic synthetic detergents are also used, which do not form ash when burned. They are called low-ash (or ashless) additives (ashless additives). Oils for modern engines usually use complex compositions that include both types of detergents. Detergents are especially active in a hot engine (this factor should be taken into account when changing the oil).
Dispersants(dispersants). Dispersants inhibit the agglomeration and sticking of oxidation products, the formation of sludge or the deposition of resinous deposits on the surface of parts. Polymers with polar groups and succinimides are commonly used as dispersants. Dispersants keep colloidal particles of oxidation products and contaminants in suspension (Fig. 1.10). Basically, they ensure the cleanliness of a cold engine. With the effective operation of dispersants, engine oil darkens, and dispersed fine oxidation products do not clog the filter and do not settle on hot engine parts.
Additional additives
Emulsifiers(emulsifiers). These compounds reduce the surface energy of liquids, as a result of which the water in the oil forms a stable emulsion and does not separate into a separate layer. Emulsifiers are detergents.
Defoamers(antifoam additives). Foaming disrupts the normal operation of the lubrication system: lubrication of rubbing surfaces becomes insufficient due to breaks in the oil film, the operation of hydraulic systems deteriorates, and the process of oil oxidation accelerates in the presence of atmospheric oxygen. Foaming is facilitated by intensive mixing of the oil. Viscous oils are more prone to foaming, especially at low temperatures and in the presence of moisture. Antioxidant and detergent additives also enhance foaming. Antifoam additives usually contain silicone oils - polyalkylsiloxanes and some other polymers. Silicone oils destroy the walls of large bubbles, and polymers reduce the number of small bubbles.
Break-in additives(running-in additives) and engine recovery (restoring additives). Conventional lubricating oils are ineffective for this purpose. For break-in, special oils are used with chemically active break-in additives, which increase the wear of the protrusions (under the greatest load) on the friction surfaces. The protrusions are aligned and run in. Break-in oils are applied for a relatively short period of time, and only until the surfaces are run in. Reducing additives are suspensions of soft metal powder (copper and tin) in oil. Such additives not only reduce the wear of friction surfaces, but in some cases also metallize them, restoring their original dimensions. However, the use of reducing additives in the composition of commercial oils for internal combustion engines, according to all automakers, is unacceptable.
The range of fuel additives includes more than 20 main types, and the number of compositions used in practice is in the hundreds. Most of them are designed to improve combustion processes.
fuel and thereby helps to reduce the toxicity of combustion products. The principal range of additives that directly or indirectly improve the environmental characteristics of the fuel is presented below:
Antioxidants, antiknock agents and ignition promoters are added to fuels at oil refineries to ensure the standardized product quality indicators.
Antiknock agents based on tetraethyl lead and ignition promoters containing alkyl nitrates are poisonous and are not commercially available.
The use of detergent additives for gasolines and diesel fuels involves several options. Additives can either be added to the fuel directly by its manufacturers, or they can be sold separately in retail sales in small packages. Fuel comes to us in Russia mainly without the addition of additives, which means that the responsibility for their regular and correct use lies with the consumer.
FEATURES OF NATIONAL GASOLINE
Why do we need detergent additives in fuel? Maybe it's better to do without them? The fact is that gasoline contains a certain amount of substances that form resins during storage. Even the highest quality of them can contain from a few tens to hundreds of milligrams of tar per liter of gasoline. And since gasoline is produced at many enterprises, from a variety of raw materials and often using simplified technology, this amount can be quite large. Diesel fuels contain even more resins than gasoline, and since resins consist of acidic substances and are very poorly soluble in fuels, they are easily deposited on metal surfaces: fuel tank walls, fuel line walls and other parts. fuel system. Getting into the combustion chamber, they burn out incompletely due to low volatility and are converted into solid deposits - soot. Carbon deposits on candles and in the combustion chamber, coking of nozzles and loss of mobility of piston rings, clogging of the carburetor, fuel lines, fuel tanks and exhaust manifold usually lead to an increase in smoke and toxicity of exhaust gases, a decrease in engine power, an increase in fuel and oil consumption, and so on. Nagar is inevitable, but its amount can be regulated - to keep the engine in a condition close to new. Let the soot be, but small. Here, detergent additives to gasoline can provide an invaluable service - a kind of means of operational regulation of fuel quality.
Fuel additives, although some of them are called "cleaners", are designed to increase the solubility of resins in gasoline or diesel fuel to prevent them from settling in the fuel system. In addition, gasoline with an additive should dissolve existing deposits, if possible, transfer the water in the fuel tank to a finely dispersed state (crush into small drops that do not interfere with fuel combustion).
GASOLINE ADDITIVES
They are recommended to be used every 2000-10000 km of the car. Depending on the type of fuel system, additives are produced for carburetor and injection engines. Carburetor additives, in addition to detergents, must also have anti-icing qualities - after all, atmospheric moisture constantly enters the carburetor, and injectors are spared from this. In addition, both those and other additives have binding properties, that is, the ability to partially bind water that has got into gasoline. But this does not mean that if a gas tank contains a liter of water, then all of it will be in a bound form.
UNIVERSAL FUEL ADDITIVES
For fuel, there are also universal additives, for example, a universal additive in gasoline, a valve cleaner and a complex additive. The scope of their application is wider than just fuel additives, and their action is mainly aimed at cleaning the entire fuel system: combustion chamber, fuel lines, intake valves, etc. Note that additives clean intake valves. If the label of any universal fuel additive says that it also cleans the exhaust valves, then the effectiveness of this agent can be doubted. Additives intensify the process of combustion of the fuel-air mixture and prevent the possible formation of carbon deposits on the exhaust valves, but they do not formally clean them. It should be noted that these additives are safe for the catalytic converter.
DIESEL FUEL ADDITIVES
Diesel fuel needs additional additives even more than gasoline. Domestic industrial technologies for the manufacture of diesel fuel have long required modernization. The main problems that arise in cars running on diesel fuel are the formation of soot in the exhaust system and high fuel consumption. Using various additives that optimize the combustion process of diesel fuel, it is possible to improve both the characteristics of the fuel itself and the operation of the engine itself. Clean the engine, that is, wash off the deposits that remain from the combustion of low-quality diesel fuel, should be done regularly. There is a special diesel injector cleaner. There is an additive to reduce soot in the exhaust. But, of course, no additives will create a miracle - an old, broken, hastily designed and randomly assembled engine cannot be transformed into the latest achievement of world engineering.
The main advantage of a diesel engine is that efficiency can be negated when using domestic diesel fuel without additives.
CLEANING ADDITIVES
DIESEL INJECTION SYSTEMS
Among them are those that are added to the fuel tank, and those that need to be poured directly into the injection system, that is, without mixing with diesel fuel. Formally, they can no longer be considered additives. It is clear that the cleaning efficiency of the injection system is higher for the latter. The first type of additive, which provides cleaning of the entire fuel system and prevents the formation of deposits in the combustion chamber and injection system, is recommended to be applied approximately every 2000 km.
The second type of additive is used by removing the fuel hose and lowering it into a can of additive, after which the engine is started. Such additives are not recommended to be added to the tank, as they can damage its inner painted layer. But on the other hand, their effect on the injection system, in particular on nozzles, can be called shock. They remove not only soot, but also varnish deposits, which can be difficult to do even with ultrasound. By the way, BMW produces just such a product in branded packaging, although its attitude towards additives is often negative.
Additives for reducing the smoke of a diesel engine and additives for lubricating plunger pairs of a high-pressure fuel pump stand apart in a number of diesel fuel additives. The former reduce exhaust smoke by improving the combustion process of the fuel and modifying its cetane number. The use of the latter may become relevant when switching to low-sulfur diesel fuel, because, as you know, fuel pump units are lubricated with diesel fuel, and a low sulfur content can lead to increased wear of plunger pairs.
TO POUR OR NOT TO POUR?
Among motorists, there is fierce debate about the benefits and futility (or even harm) of cleaning additives in fuel. In this case, very often the negative effect of the additive is caused by its improper operation. Examples of this are legion. Here is a case described in one of the automotive forums.
“The additive is poured into the tank, the debut usually occurs when traction deteriorates, the “intellectual owner” receives extremely valuable advice in the “garage from the men” that “there is such garbage that is poured with gasoline, and the engine immediately runs like clockwork” . Our owner buys what the seller advises him, usually this happens in accordance with the availability of the seller. A friend buys 2 vials just in case, both of these vials are poured into the tank, as you know, you won’t spoil the porridge with oil, then a gradual deterioration in engine operation, a stop, a visit to a car service, replacement of nozzles, a distributor dispenser, a starting injector. We will not describe the feelings of the delighted car owner, we will only note that pregnancy can be cured with a large amount of laxative, but usually a positive effect can occur in this regard only in the column: “side effects”. What happened in the belly of the "horse" after filling the additive? As you know, there are "good" and "bad" producers. Additives produced by "bad" manufacturers differ little in composition from additives produced by "good" manufacturers. The difference is observed mainly in the exact observance of the drug formulation. If we fill in an injector cleaner made by some "reputable company" (Wynn's, Liquimoly, ICS, Pingo), we can be sure that we will get the same thing that we got last time and will get 1000 times after. If we use an additive of the “left property”, its action will be very sharp, especially if the concentration is exceeded by more than 20%. That is, instead of a smooth, layered, “gentle” washing off of dirt, our additive begins to wash off the dirt in pieces. The process starts in the gas tank. Because the process goes very quickly due to the increase in concentration, the “beaten off” pieces of dirt and the dregs raised from the bottom of the tank instantly clog the fuel filter. If the pump gives good pressure, and the fuel filter was purchased according to the residual financing principle, the filter element may tear, and all the contents of the filter fall into what is popularly called the "injector". Naturally, this is a special case, but I think every motorist will remember the person who told him a similar story.
DON'T POISON YOUR LOVE!
How to choose a detergent additive in the fuel so that it is not the last thing that the engine of your favorite car will take inside? Here are some tips:
When choosing an additive, you should pay attention to the following points:
Give preference to additives from a manufacturer that produces different products for fuel systems with carburetors and separately (!) For systems with injectors.
Additional points when choosing will give the manufacturer the presence in the range of individual additives for gasoline engines with direct injection GDi.
For the first application (the first two tanks of fuel), it is better to use half the additive concentration recommended by the manufacturer. Then the maximum (during the period of one or two tanks of fuel). After that, you can switch back to half concentration (to maintain the established minimum level of deposits and impurities).
To keep the fuel system clean, the additive must be filled in regularly, that is, every 5-6 full-weight gas stations. There are statements that the use of cleaning additives adversely affects candles, therefore, in the case of long-term candles, it is better to use the services of companies that clean the fuel system at special installations.
According to the site www.potrebitel.ru
The currently offered fuel additives include over 20 main types, and the number of compositions used in practice is in the hundreds. Most of them use substances designed to improve fuel combustion processes. And thus they help to reduce the toxicity of combustion products.
The main range of additives designed to directly or indirectly improve the characteristics of the fuel is represented by products that can be used at manufacturers or independently.
Types and use of additives
Antiknock agents, antioxidants and ignition promoters are added to the fuel at the refinery to ensure product quality is within the specified range. Antiknock agents are based on tetraethyl lead, and ignition promoters contain alkyl nitrates, so they are extremely poisonous and are not sold at retail.
Detergents and diesel fuel are used in several versions. Additives can be added to the fuel either directly by its manufacturers, or they can be retailed separately in small packages. it is mostly sold without added additives, which means that the responsibility for the regularity and correctness of their use lies with the consumer.
How to choose a safe additive
You should start with the fact that gasoline without additives, firstly, is not on sale (it quickly loses its properties). In addition, absolutely all additives that exist today are poisonous, although to varying degrees. At the refinery, they are added to gasoline in the complex and in the required proportion. Therefore, by adding an additive to high-quality fuel, you can harm the car, by exceeding the concentration of a “useful” substance, you can make it harmful.
If low-quality fuel is poured into the tank, it must be drained without trying to improve it with additives.
Experts are unanimous in this opinion and numerous tests conducted by a number of specialists, both professionals and amateurs, confirm this. No matter how strangling the green amphibian, it is better to do less. Even with the correct use of good quality additives, the engine will definitely respond to bad fuel. It's like seasoning for spoiled meat - the taste and smell are pleasant, but the body will not slow down with an unambiguous response to such an attitude towards it.

In a rare case, if the required fuel is not on sale, you can increase the octane number by 1.2-1.7 units by adding an additive. However, tests published in the media indicate that the effect is only possible from additives containing iron and an amine antiknock.
The car relatively painlessly perceives only detergents sold under brands of well-known manufacturers.
Their classification is as follows:
- fuel system cleaners;
- combustion chamber cleaners.
The composition of these additives in the fuel usually includes: corrosion inhibitors, and detergent components (most often these are surfactants). Such a composition is able to “loosen” soot and deposits, and small particles leave with the flow fuel mixture into the cylinder and there safely burn out.
But experts do not recommend using them on older cars. The desire to do the best can turn into traditional as always. During the long operation of the car, too many insoluble deposits usually accumulate in it.
Under the influence of the active formula of the complex cleaner, all dirt and solid deposits peel off from the surface of the tank and pipeline. As a result, there is a danger that all the dirt will get along with the fuel into the fuel system of the car. As a result, clogging of the curtains of the filter elements and failure of the fuel equipment is possible.
What is bad for a car
The set of additives in different markets specializing in the sale of spare parts is approximately the same markets, and among them there are many outlets selling products harmful to vehicle systems. Unfortunately, according to existing legislation, this product is not subject to certification.
Naturally, the composition is not written in capital letters on any label, only the trade name is visible on the packaging. The only solution is to carefully read the composition. For example, an additive of up to 30% (a tablet added to gasoline) is proposed, the main active ingredient, naphthalene, is harmful to the fuel system. However, the liquid is provided with only a small inscription "ethyl". And you can’t say that this is not true - ethyl is really there.

It is interesting to observe the reaction of sellers to whom you are trying to explain that the product they offer is harmful to the engine. They are ready to fight for their belief that this chemistry is completely safe. One of the arguments in its favor is that That the product is ISO certified. But after all, no one is going to dispute that the same naphthalene really meets all the standards, as well as technical alcohol with a blue label. However, this does not in the least make it less aggressive towards engine parts.
And the source of chemicals for the preparation of additives from scammers has nothing to do with the technological process of production. On the Internet, you can find hundreds of offers of various reagents. Moreover, with a wholesale order, sellers will also deliver the goods to any place. For what chemical components are used, it is not even asked.
Additives in gasoline
Carburetor additives, in addition to detergent functions, also have anti-icing qualities.
Since the presence of moisture in the atmosphere constantly affects the carburetor, accumulating on its working surfaces. Injectors are free from this problem. In addition, additives of both types have binding properties, that is, they have the ability to bind, albeit partially, water that has got into gasoline. This does not mean, of course, that if you add a liter of water to the gas tank, then it will all be in a bound form. However, this allows you to quite reliably protect yourself from the resulting condensate.
Universal additives
There are also universal additives for fuel, for example, a universal additive for gasoline, a complex additive and a valve cleaner. The scope of such products is wider than just an additive to the fuel, and the action of their constituent reagents is mainly aimed at cleaning the fuel system.
Combustion chambers, fuel lines, intake valves and other similar parts of the car are subjected to cleaning. It is worth noting that only intake valves are cleaned with additives. If any product has an inscription on the label that it can also clean exhaust valves, then the effectiveness and reliability of such a product is highly questionable.

Additives are able to intensify the combustion process of the fuel-air mixture and prevent the formation of soot on the exhaust valves, but they do not clean them. It should also be noted that universal additives are safe for the exhaust gas converter.
Diesel fuel additives
Diesel fuel needs additives even more than gasoline. The domestic industry has a technology for producing diesel fuel, which has long required modernization. The main problems that arise in cars running on domestic diesel fuel are the formation of soot in the gas exhaust system and an increase in fuel consumption. Using additives available on the market, it is possible to optimize the combustion process of diesel fuel, improve both the characteristics of the fuel itself and the operation of the engine.
It is necessary to regularly clean the engine, that is, wash off the accumulated deposits left over from the combustion of diesel fuel.
A special cleaner for diesel injectors is produced. There is an additive on sale that allows you to reduce the amount of soot in the exhaust. But, no additives can do a miracle, and it is impossible to get the same running performance from an old, broken, hastily designed and poorly assembled engine as from a representative of the latest achievements of world engineering.
Main advantage diesel engines in their economy. But it can be reduced to zero as a result of the use of domestic diesel fuel that is not supplied with additives.
Diesel injection cleaning additives
Among the additives that allow you to clean the injection system, two types can be distinguished:
- added to the fuel tank;
- not miscible with fuel.
The last ones on the list are those that are poured directly into the injection system. The first type of additive cleans the entire fuel system at once and prevents the formation of deposits in the injection system and combustion chamber. It is recommended to apply after about 2000 km.
The second type of fuel additive is used in a special way. Remove the fuel hose, lower it into a container with an additive and start the engine. Such an additive is not recommended to be added to the tank, as it can damage the painted inner layer. But on the other hand, its effectiveness in cleaning the injection system, especially injectors, can be considered shock. They clean not only soot, but also varnish deposits, which can be especially difficult to do.

Apart from a number of additives for diesel fuel are additives that reduce engine smoke and additives that lubricate the plunger pairs in the high pressure fuel pump. The former reduce exhaust smoke by improving the combustion process of the fuel and changing its cetane number. The use of the second types of additives can be recommended when switching to low sulfur fuel.
- Methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE)
- Pluses: high own octane number (more than 110 units), which is useful for the engine: the contained oxygen ensures greater combustion efficiency and reduces CO and CH emissions.
- Cons: high content of MTBE (more than 15%) leads to a decrease in power and an increase in the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx).
In addition, gasoline with MTBE is aggressive to fuel system seals and increases the rate of corrosion.
- Monomethylaniline (MMA)
- Pros: In concentrations up to 1.3% harmless, reduces detonation.
- Cons: The increased content in the engine forms deposits, the valves often “hang”.
- Detergent additives
- Pros: a balanced package containing corrosion inhibitors, demulsifiers (water absorbers) and detergent components are carried away in the air-fuel mixture flow and burn safely in the cylinder.
- Cons: an overdose (over 10%) leads to a malfunction of the engine, it will not start

Video about fuel additives
Conclusion!
Tell all readers here how you use fuel additives in your car. Personal experience and own feelings are much better than the most detailed instructions.
Varsovia - an expensive hybrid sedan from Poland
The design of the car was carried out by the design bureau Kadler, located in the suburbs of Warsaw. According to the designers, they were inspired by… mermaids! Which explains the unusual corrugated sides and front of the car, which, according to the designers, look like mermaid scales. The interior looks even more unusual, in which there is no front passenger seat, but instead ...
Moscow will soon start fines for parking on lawns
According to the press service of MADI, certification of the updated Mobile Inspector application, which is used by inspectors on foot, is currently being completed. After the update, it will be possible to punish violators who park on lawns, according to m24.ru. The information that the MADI inspectors will automatically record will be sent to their own information system, where ...
Drunk driving: the traffic police wants to introduce a test for an idiot
We are talking about a special "medical support", similar to the Idiotentest practiced in Germany ("idiot test"). Vladimir Kuzin, deputy head of the traffic police of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation, spoke about this on the air of the Vesti FM radio station. In Germany, if a driver scores a certain number of demerit points for committed offenses or drunk driving, he is sent to a special medical and psychological examination (MPU), ...
Russian designer who painted Chiron left Bugatti
At Bugatti, Alexander Selipanov (whom even the bosses of the concern usually called Sasha) served as chief exterior designer. Appearance of the conceptual Bugatti Vision Gran Turismo and serial hypercar Chiron - Selipanov's creations. It is known that the Russian, who graduated from the American Art Center College of Design in the direction of transport design, worked ...
Updated Amarok: first hints from Volkswagen
Recall that the premiere of the Volkswagen Amarok pickup truck took place in the winter of 2009-2010, and therefore many predicted a middle-aged model for a quick generational change. However, contrary to these predictions, Amarok is just waiting for an update, as evidenced by pictures of a camouflaged car taken during road tests. The teasers distributed by the Volkswagen press service do not contradict this information: ...
As explained in the official statement of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, in both cases the decision was made in connection with the voluntary refusal of the subject of the insurance business to carry out the activities provided for by licenses and comes into force from the day it is published in the Bulletin of the Bank of Russia. Thus, the number of OSAGO insurers continues to decrease in Russia. At the beginning of August 2016...
Electric vehicles: there are only a few hundred of them in Russia
The largest share (36.6%) falls on the Mitsubishi i-MiEV electric hatchback, of which 237 units are registered. Recall that the Japanese electric car on Russian market will be sold officially, and therefore success is quite natural. In second and third place are Tesla Model S and Nissan Leaf, which sold almost the same circulation - 152 and 145 copies, ...
Which sedan to choose: Camry, Mazda6, Accord, Malibu or Optima
Powerful story The name "Chevrolet" is the very history of the formation of American cars. The name "Malibu" beckons with its beaches, where numerous films and television series were filmed. Nevertheless, from the first minutes in the car "Chevrolet Malibu" one can feel the prose of life. Pretty simple stuff...
Choice of affordable sedan: Zaz Change, Lada Granta and Renault Logan
Some 2-3 years ago it was considered a priori that an affordable car should have a manual transmission. Their destiny was considered a five-speed mechanics. However, things have now changed drastically. First, they installed a machine gun on the Logan, a little later - on the Ukrainian Chance, and ...
What's on the outside Big-eyed and extravagant "Nisan-Juk" does not even try to look like a respectable off-road vehicle, because this car is full of boyish enthusiasm. This machine can not leave anyone indifferent. She either likes it or she doesn't. According to the certificate, it is a passenger station wagon, however ...
The best cars of 2017 in different classes: Hatchback, SUV, Sports car, Pickup, Crossover, Minivan, Sedan
Let's look at the latest innovations in the Russian automotive market in order to determine best car 2017. To do this, consider forty-nine models, which are distributed among thirteen classes. So, we offer only the best cars, so it is impossible for a buyer to make a mistake when choosing a new car. Best...
Fast cars are an example of the fact that automakers are constantly improving the systems of their cars and are periodically developing to create the perfect and fastest vehicle for movement. Many of the technologies that are developed to create a super fast car later go into mass production ...
HOW to choose and buy a car, Buying and selling.
How to choose and buy a car The choice of cars, both new and used, on the market is huge. And not to get lost in this abundance will help common sense and a practical approach to choosing a car. Do not give in to the first desire to buy the car you like, carefully study everything ...
Rating 2017: DVRs with a radar detectorThe requirements for additional equipment in the passenger compartment are growing at a rapid pace. Up to the fact that in the cabin there is simply not enough space to accommodate all the necessary equipment. If earlier only video recorders and air flavors interfered with the review, today the list of devices ...
- Discussion
- In contact with
Issue Status
The Russian fleet of passenger cars has about 26 million units, of which more than 50% have been in operation for over 10 years. In terms of environmental performance, 75% of passenger cars comply with Euro-1 and Euro-2 standards; 60% of trucks are Euro-0. According to the forecasts of the Federal Highway Agency, the number of cars by 2015 will increase to 42-47 million units, mainly due to foreign cars. The requirements for emissions of harmful (polluting) substances by motor vehicles put into circulation on the territory of the Russian Federation are determined by the Technical Regulations adopted on October 12, 2005, and the deadlines for the introduction of technical standards are set: Euro-2 - April 22, 2006; Euro 3 - January 1, 2008; Euro 4 - January 1, 2010; Euro 5 -January 1, 2014 Today, Russia is lagging behind Europe in terms of meeting the emission toxicity requirements. Ensuring and maintaining the environmental characteristics of the car during operation is possible only if high-quality motor fuels are used.
The renewal of the fleet is a long process, and in this situation, the use of gasoline with detergents and multifunctional additives on Russian vehicles will ensure a significant reduction in harmful emissions into the atmosphere and improve the environmental situation. The effect of detergent additives on the operational efficiency of the engine and the toxicity of exhaust gases has been proven by many works and tests carried out not only abroad, but also in Russia. The results of road tests conducted by BASF on Western European vehicles showed that the use of motor gasolines with multifunctional additives provides an average reduction in the content of hydrocarbons in the exhaust gases: hydrocarbons - by 20, CO - by 24, (N0)x - by 13 and CO2 - on 2% .
Abroad, the addition of detergents and multifunctional additives to motor gasolines is widespread. In accordance with the clean air law, from January
1995 All motor gasolines used in the US must contain detergent additives. In European countries, there are no requirements for the mandatory addition of detergent additives. The Technical Committee of Additive Manufacturers in Europe (ATC) does not see the need for legislative regulation of the use of fuel additives, since the US experience has shown that legislative regulation is inferior to the market in terms of efficiency. Despite the lack of such regulation in Europe, detergents and multifunctional additives are widely used there; as a rule, they are added to gasoline at terminals directly to fuel trucks when sending fuel to filling stations.
Work on the creation of detergent and multifunctional additives for motor gasoline has been carried out in Russia for more than thirty years. For a number of years, domestic multifunctional additives Afen and Avtomat, used for carburetor engines, have been produced on an industrial scale. In NORSI, the production of gasolines with these additives was also organized. At present, due to the lack of raw materials, additives Afen and Avtomat are not produced.
In order to improve the ecological situation in Moscow and Tatarstan, decisions were made to produce motor gasoline with detergent additives. Thus, in accordance with the order of the Mayor of Moscow from January 1998, all motor gasoline sold in Moscow had to contain detergent additives. For this purpose, specifications were developed for city gasolines, tests were carried out on gasolines from the Moscow Oil Refinery with multifunctional additives, and approvals for their production were issued. However, the decisions made are not our implementation, partly due to the lack of production of domestic additives, but to a greater extent, in our opinion, due to the lack of economic incentives.
Russian, as well as European, specifications for motor gasolines allow the addition of additives, including detergents, that improve their performance properties, but this is not fixed by law.
In the annex to the technical regulation "On the requirements for emissions of harmful (polluting) substances by automotive equipment put into circulation in the Russian Federation", along with other fuel characteristics, the indicator "Deposits on intake valves and combustion chamber" is introduced. According to this indicator, gasoline for Euro-3 and Euro-4 cars should correspond to European gasolines of a similar class. At present, in Russia, as well as in Europe, there are neither temporary nor permanent standards that characterize the cleaning properties of commercial gasoline.
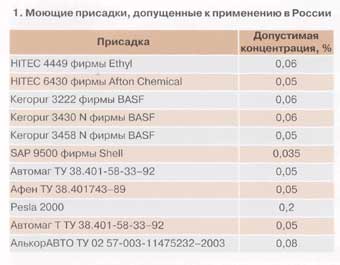
Until recently, motor gasolines with detergents and multifunctional additives were practically not produced in Russia, although many enterprises have permits for their production. The list of the main additives approved by the MVK for use in the composition of motor gasoline in Russia is given in Table. 1.
Ecological issues are especially relevant for Moscow, as for any metropolis with a high concentration of vehicles. The Government of Moscow adopted a resolution (No. 952-PP dated December 28, 2004), according to which all high-octane motor gasolines sold in the city from January 1, 2006 must contain detergent additives. Despite the fact that the legality of this regulation is still discussed in the press, it helped to attract the attention of manufacturers to detergent additives and the problem of improving the environmental friendliness of produced fuels.
Implementation of programs for the production of competitive motor fuels
The oil companies BP-TNK, LUKOIL, YUKOS have adopted programs aimed at organizing the production of gasoline for Euro-3 and Euro-4 vehicles, including those with detergent additives. Taking into account the different interpretations of the term “detergent additive”, it should be noted that today we are talking about multifunctional additive packages containing a detergent component, corrosion inhibitors, demulsifiers and other components, as well as a carrier fluid on a mineral, synthetic or semi-synthetic basis.
In recent years, research in the field of detergent additives has noticeably intensified in Russian research institutes. JSC VNII NP, together with foreign manufacturers of fuel additives, is carrying out work on organizing the industrial production of motor gasolines with detergents and multifunctional additives in Russia.
In 2004, the institute developed a bench method for assessing the tendency of gasolines, including those with additives, to form deposits in the engine intake system (STO ANN 40488460-001-2004). Tests according to this method are carried out on a full-size VAZ-2101 engine in comparison with the original gasoline. The duration of the tests is 12 hours (two six-hour cycles with a break of 18 hours). The test conditions and the adopted evaluation criteria provide a clear indication of the effect of the introduction of a detergent additive.
In order to organize the production of modern competitive motor fuels using this method, recommendations were developed for a number of oil refineries on the production of motor gasolines with detergent additives. At the same time, foreign additives widely represented on the Russian market were recommended: Keropur 3430 N and Keropur 3458 N (BASF), HITEC 6430 (Afton Chemical) and domestic - AlcorAVTO.
NK YUKOS is one of the first companies that responded to the decision of the Moscow government. In 2005, a technology was developed at the Novokuibyshevsk Refinery, tests were carried out and put into production of Regular Euro-92 and Premium Euro-95 gasolines with multifunctional additives AlcorAVTO and Keropur 3430 N (BASF) for Euro-3 class vehicles. In 2006, qualification and bench tests of gasoline produced by the Kuibyshev and Syzran refineries with Keropur 3458 N, HITEC 6430 and AlcorAVTO additives for Euro-4 class vehicles were carried out.
Positive results were obtained when testing gasolines Regular Euro-92/4, Premium Euro-95/4 and Super Euro-98/4 from the Ryazan NPK and Premium Euro-95/4 manufactured by Kirishinefteorgsintez with Keropur 3430 N and Keropur 3458 N additives for Euro-4 cars.
The effect of detergent additives on the tendency of gasolines to form deposits in the carburetor, on the intake valves and the combustion chamber is illustrated by the results of bench tests given in Table. 2.
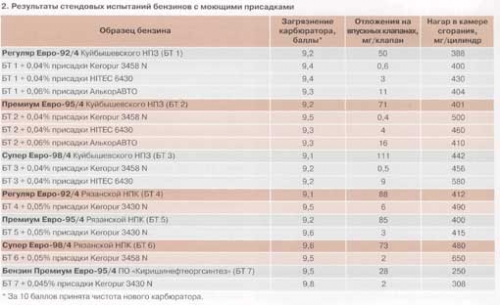
In table. 3 shows the component compositions of base gasolines. The test results confirm the high ability of Keropur 3430 N, Keropur 3458 N, HITEC 6430 and AlcorAVTO additives to keep the carburetor and intake valves clean, while their addition to gasolines leads to an increase in the amount of carbon deposits in the engine combustion chamber. It should be noted that all modern detergent additives are high-molecular compounds in composition with a carrier oil and, having good detergent properties, lead to an increase in carbon deposits in the combustion chamber. As can be seen from Table. 2, for all tested additives, the amount of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, in relation to base gasolines, exceeds 140%, which corresponds to the recommendations of the World Fuel Charter.
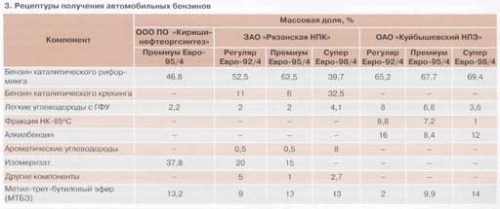
In addition to high functional efficiency, additives must meet the requirements that determine the possibility of their introduction into gasoline and its use in operating conditions. The additive should not impair the physicochemical and performance properties of gasoline, and be fully compatible with other additives.
Qualification testing of prototypes showed that the addition of Keropur 3430 N, Keropur 3458 N, HITEC 6430 and AlcorAVTO additives does not adversely affect the physicochemical and performance properties of gasolines with additives and their quality fully complies with the requirements of GOST, TU (Table 4). At the same time, testing of gasolines with additives according to the methods provided for by the set of methods for the qualification assessment of motor gasolines (KMKO) revealed a number of features. The addition of tested additives to gasolines leads to an increase in the total content of oxidation products (GOST 22054-76) and the content of actual resins determined after contact with rubber (the method is approved by the decision
GMK No. 23/1-122 dated 07/05/85)
As mentioned above, all latest generation detergents and multifunctional additives are high molecular weight compounds formulated with a carrier oil. After the gasoline is evaporated, any additives having a high molecular weight partially remain in the residue. The change in the total content of oxidation products and actual resins after contact with rubber is due to the fact that these tests use the method for determining actual resins according to Budarov (GOST 8489). For the analysis of gasoline, methods similar to GOST 8489 are currently not used anywhere. The actual resins determined according to this GOST are a non-evaporated residue, since it is not washed with heptane, as provided by GOST 1567.
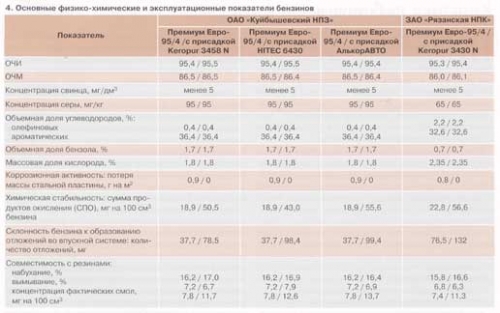
The presence of additives in gasoline also causes an increase in the amount of deposits in the intake system (the method was approved by the GMK decision No. 23/1-78 of 05/17/78). This increase is due to the formation of an adsorption film on the plate after the evaporation of gasoline, while the amount of adsorbed additive is comparable to the amount of deposits determined by this method.
Thus, not all of the test methods included in the CCL allow a reliable assessment if a detergent additive is present in gasoline. An analysis of the norms and methods of the current KMKO motor gasoline shows that they are based on the requirements of technology 25-30 years ago and require revision.
Based on the research and testing conducted, gasoline produced by the Ryazan Oil and Gas Refinery, Kuibyshev, Novokuibyshev, Novo-Ufimsky oil refineries, Angarsk petrochemical complex and Kirishinefteorgsintez with foreign additives Keropur 3430 N, Keropur 3458 N, HITEC 6430 and domestic AlcorAVTO are approved by MVK for production and use on automotive technology.
The Moscow Oil Refinery and the Ryazan Oil and Gas Refinery have already started production of motor gasolines with detergent additives for Euro-3 and Euro-4 vehicles.
In order to produce competitive motor fuels, Russian oil companies, as well as European manufacturers, have begun to use detergent additives to create fuel "brands". Ultimate gasoline from TNK-BP and EKTO from LUKOIL have been developed and have already entered the market.
Today, the necessary regulatory and technical base has been created in Russia, which makes it possible to ensure the production of commercial motor gasoline with detergent additives that meets modern European requirements.
Bibliography
1. Nikitina E.A., Golovanov M.L. // World of petroleum products. 2006. No. 5. S. 12-19.
2. Nikitina E.A., Emelyanov V.E., Andreev S.V. // World of petroleum products. 2006. No. 2. S. 25 29.
3. Nechaev V.K., Manaenkov V.M., Bakaleinik A.M. // Mirnefteproducts. 2006. No. 2. S. 30-32.
4. Nikitina E.A., Emelyanov V.E., Alekseeva S.I. etc. // World of oil products. 2006. No. 1. S. 2
E.A. NIKITINA, Ph.D. tech. Sciences,
V.E.EMELYANOV, Doctor of Engineering Sciences,
V.M. MANAYENKOV,
A.M. GROCCER, Ph.D. tech sciences,
S.I. ALEKSEEVA
(JSC VNII NP)
Magazine "World of Petroleum Products" №1, 2007
Content
Engine flush
Often, when buying detergent additives in engine oil, car owners hope for a miracle that their use will entail. Indeed, this type of additive has a positive effect on the condition of the engine, but you must strictly follow the instructions and know a few application halts. Otherwise, the car may be damaged.
How additives work
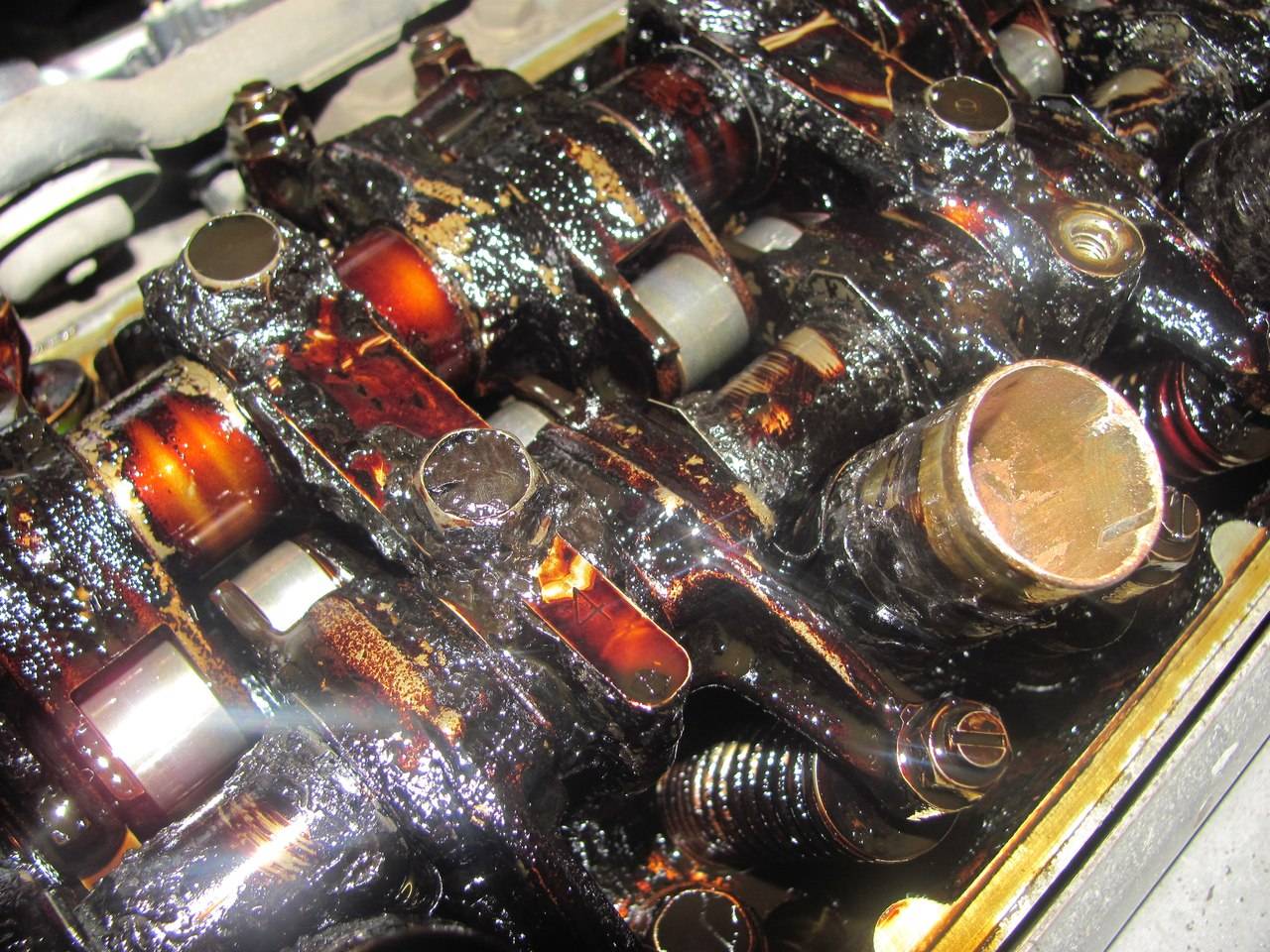

Cylinder head requiring flushing
Detergent additives usually contain two components: detergent and dispersant. The first separates combustion products and other slags from engine parts and sends them to the filter. And the dispersing components do not allow dirt to gather into large lumps and burn to the mechanisms.
Various substances are used as detergents. These may be alkyl salicates, sulfonates or sulfophenates. Each of them can be used in a separate type of additives, and can be combined with others. As for the principle of their action, we can say that it is the same as that of a simple tool that is used to wash dishes in the kitchen. But besides this, detergents have the properties of alkali, that is, they neutralize acids.
Where does acid come from in an engine? It is formed from the combustion of sulfur, which in turn is contained in the fuel. And in diesel it is more than in gasoline. In addition, sulfur is produced during the oxidation of oil. As long as the acid is neutralized with detergent, the engine will not corrode. That is why the second task of detergent additives in oil is called corrosion protection and removal of acids.
When buying a detergent, it is best to purchase one based on alkyl salicates, since their characteristics are better at removing dirt, tar and slag from engine parts.
As for dispersants, which are also included in the composition of detergent additives, their purpose is to dissolve large deposits and prevent carbon deposits and oxidation products from settling on engine parts. Due to the fact that contaminants can stick together in lumps, the oil becomes viscous, the filter is blocked by soot products, which make it difficult for oil to access parts.
When all deposits pass through the lubrication system, they eventually settle on the filter. After detergent additives are added to engine oil, the filter turns black from combustion products, and the oil itself becomes dark. This is all the result of the action of additives in the oil. After that, the lubricant should be changed again.
Proper engine flush
To flush the motor, the modern auto chemical goods market offers a wide variety of additives. The so-called "fifteen minutes" are popular. These are additives that a motorist can use on their own, having a pit in the garage.

Engine flush procedure
You can use two options for cleaning the motor. The first is to apply a full volume additive. To do this, drain the oil in the car, then pour additives into the oil to flush the engine. It is not necessary to change the filter with this cleaning option. Then we leave the car to work on Idling. After 15-20 minutes, the car must be turned off. OK it's all over Now. Then the usual procedure for changing the oil: drain what was filled, change the filter and fill in a new one.
This method could be called good, if not for one BUT ... After the cleaning procedure, a certain amount of additive remained in the engine, which in itself is a liquid composition. So, when combined with new oil, it will dilute the viscosity of the lubricating fluid, which, of course, will adversely affect the characteristics of fresh oil.
There is also a second way to clean the motor. The additive should be poured into the old oil and leave the car to idle. And then we drain everything, change the filter and fill in new oil. With this procedure, kerosene, which is the basis of the additive, evaporates half an hour after the engine is running.
In addition, the old oil has already worked out its life, which means that it does not contain enough detergents. And a new additive added to the old oil fills this gap, forcing the oil to work in an increased activity mode. And by thinning the oil, the additive thereby allows carbon deposits to move more freely through the oil system and out of it.
But you can wash the engine better only in a car service. The so-called professional washes have a high concentration of detergents. Therefore, in a short period of time, they dissolve everything that has accumulated on the walls of engine parts: carbon deposits, coke, varnish deposits. This composition of the additive in the oil for flushing is used only in car dealerships, since its use is associated with safety precautions.
Here, the car owner will be helped to determine how much the gearbox needs to be flushed. By the way, it is not at all easy to flush transformers in automatic transmissions. Therefore, it is best to entrust this procedure to professionals in a car dealership.

Engine flush oil
An example of punishable amateur activity is the case when a car enthusiast bought an Opel Frontera car from his hands and decided to flush its engine. And after a while the car just stood on the road. As it turned out, the additive did its job, cleaning the engine so that the fronter oil, or rather the products of its combustion, clogged the filter, the oil scraper mesh, which did not allow the lubricating fluid to pass through. As a result, engine parts could not stand the work without lubricating fluid and failed.
